Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How does the wear and life of the shearing machine affect production costs and production efficiency?
The wear and life of the shearing machine have a direct and significant impact on production costs and production efficiency. The shearing machine is a high-load, high-frequency operation equipment. Long-term use will cause its components (especially the tool, hydraulic system, drive device, etc.) to wear. The following are several aspects of how wear and life affect production costs and production efficiency:
1. Production efficiency
Decrease in shearing accuracy: The wear of the shearing machine tool will lead to reduced shearing accuracy, the cutting surface may become uneven, there are too many burrs, and even lead to incomplete material cutting. This will not only reduce production efficiency, but also increase subsequent processing steps (such as deburring, trimming, etc.), thereby delaying the production cycle.
Downtime: When the tool is severely worn, it may need to be replaced or sharpened frequently. Each tool replacement will cause the equipment to stop. Such downtime will directly affect the continuity and efficiency of production. Especially in large-scale production, the increase in downtime has a more obvious impact on the overall production efficiency.
Slow down the operation speed: When the shearing quality decreases due to tool wear, it may be necessary to reduce the shearing speed to avoid unqualified products. This slowing down operation not only affects production efficiency, but may also lead to a decrease in production capacity and an inability to meet demand.
2. Production cost
The cost of maintaining and replacing tools: Wear is an inevitable natural phenomenon of shearing machine equipment, but the wear of key components such as tools will increase maintenance costs. When the tool wears to a certain extent and needs to be replaced, the cost of replacing the tool is usually high, especially for tools made of high-precision or high-hardness materials, the cost will increase further. In addition, frequent tool replacement and repairs also require downtime, adding unnecessary costs to the production process.
Repair and maintenance costs: Wear is not limited to tools. Other components such as hydraulic systems and drive systems will also wear out during long-term use. These wears may cause system efficiency to decline or fail, requiring regular maintenance and repairs, which in turn increases the maintenance cost and labor cost of the equipment. If wear causes equipment failure, other high-priced components (such as hydraulic pumps, motors, etc.) may also need to be replaced, adding additional maintenance costs.
Scrap and rework costs: The reduction in cutting quality caused by tool wear often produces unqualified products. These scraps not only increase material waste, but may also require additional time and expenses for rework or reprocessing. This not only directly increases production costs, but may also affect product delivery, further increasing indirect production costs.
3. Product quality and market competitiveness
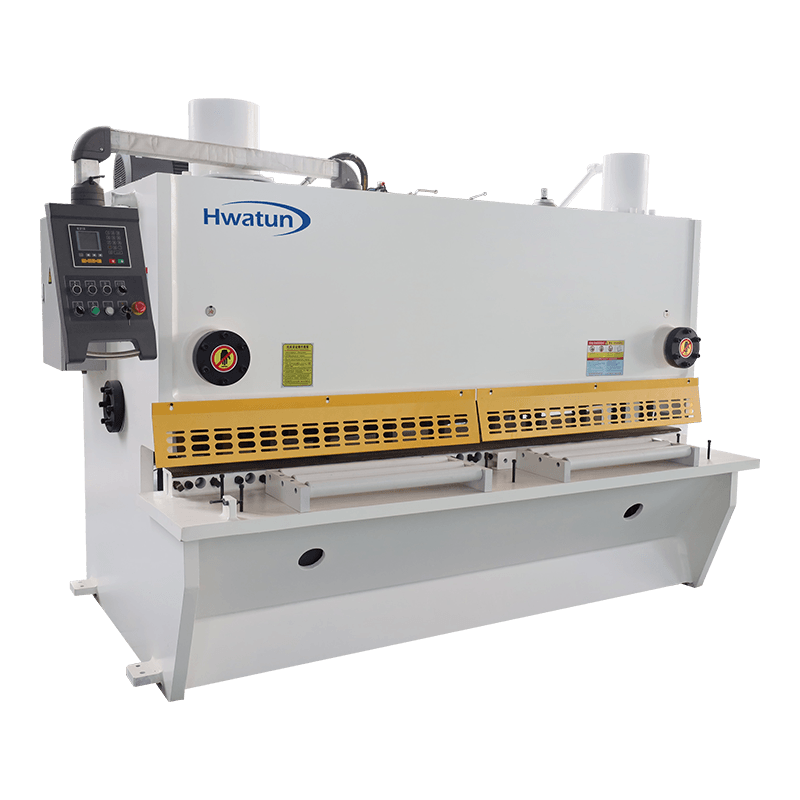

Affecting product quality: Wear of shears usually leads to reduced cutting accuracy and unstable product quality. Low-quality shearing will lead to more burrs, larger dimensional errors, incomplete cutting and other problems, affecting the quality of the final product. In many industries with strict quality requirements (such as aviation, automobiles, electronics, etc.), the decline in product quality may lead to returns, customer complaints, and even affect the company's brand reputation and market competitiveness.
Decreased market competitiveness: In the fierce market competition, product quality and production efficiency are the key to competition. If the shearing is inaccurate and the production cycle is extended due to wear, it may affect the timeliness and quality of product delivery, and then affect the company's competitive position. Especially in the face of highly customized or high-precision requirements of customer needs, the wear of shears may become a serious constraint.
4. Energy consumption and environmental impact
Increased energy consumption: Severely worn shears usually require more power to maintain the same workload. For example, tool wear increases the resistance to cutting, resulting in an increased burden on the drive system, and the motor may need to consume more power to complete the shearing task. Therefore, wear and tear will not only affect production efficiency, but also increase energy consumption per unit product, further increasing production costs.
Environmental impact: The reduced efficiency and energy waste caused by wear and tear may increase the operating time and energy consumption of the equipment, thus having a negative impact on the environment. In the current context of promoting green manufacturing and sustainable development, this additional energy consumption and environmental burden may cause companies to face more regulatory and environmental pressures.
5. Service life and return on investment
Shortening equipment service life: If the wear and tear of the shearing machine is not maintained and repaired in time, the overall service life of the equipment will be shortened. This means that the company needs to invest money in advance to replace the equipment, increasing the capital expenditure of the equipment. At the same time, frequent equipment upgrades also mean that the investment return cycle will become longer, resulting in a longer recovery time for funds.
Depreciation and reinvestment: The shearing machine will wear and tear during use, causing its performance to gradually decline, and eventually need to be replaced with new equipment or parts. If the maintenance is not appropriate, the depreciation rate of the equipment will accelerate, and the company will need to invest more money in equipment renewal and replacement, increasing the pressure of reinvestment.
6. Prediction and optimization management
Wear prediction and planned maintenance: Through real-time monitoring and data analysis of shear wear, enterprises can predict the trend of wear in advance, so as to take preventive measures to avoid excessive wear and failure of equipment. Regular preventive maintenance can effectively reduce downtime and maintenance costs caused by wear, ensure long-term stable operation of equipment, thereby improving production efficiency and reducing the incidence of unexpected failures.
Intelligence and automation: Modern shears are gradually developing in the direction of intelligence and automation. By introducing sensors, Internet of Things technology, artificial intelligence, etc., the wear status of equipment can be monitored in real time and working parameters can be automatically adjusted to minimize efficiency loss and quality fluctuations caused by wear.
The wear and life of the shear directly affect production efficiency, product quality, production cost and enterprise competitiveness. Problems such as reduced precision, equipment downtime, increased maintenance and repair costs, and waste generation caused by wear will reduce production efficiency and increase production costs. In order to maximize the return on investment of shears, enterprises need to strengthen regular maintenance of equipment, adopt advanced technology for wear monitoring, and rationally plan equipment replacement cycles to ensure that the equipment maintains optimal operating conditions throughout its life cycle, thereby improving production efficiency, reducing overall costs, and enhancing market competitiveness.
News categories
Product categories
Related Products
 +86-159 5138 1316
+86-159 5138 1316 +86 180 6819 3096
+86 180 6819 3096 [email protected]
[email protected] Group 4, Xinba Village, Binhai New Area (jiaoxie Town), Laoba Port, Nantong City, Jiangsu, China.
Group 4, Xinba Village, Binhai New Area (jiaoxie Town), Laoba Port, Nantong City, Jiangsu, China.
Copyright © Nantong Hwatun Heavy Machine Tool Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

 Eng
Eng  简体中文
简体中文 Español
Español русский
русский







