Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
How to improve the overall vibration resistance of Shearing Machine by improving the support system?
Improving the overall vibration resistance of the shearing machine is the key to optimizing equipment performance, extending service life and improving processing accuracy. By improving the support system, the impact of vibration on the equipment can be effectively reduced.
1. Optimize the frame structure design
Increase rigidity: The frame structure of the shearing machine is the core part of the support system. By increasing the thickness of the frame or using high-strength materials (such as cast steel or high-strength alloy steel), the overall rigidity can be significantly improved, thereby reducing vibration.
Strengthen the connection parts: The welding or bolted connection parts of the frame are usually the weak points of vibration. By optimizing the welding process (such as using low-hydrogen welding rods or preheating treatment) or increasing the number and strength of the connecting parts, the possibility of vibration transmission can be reduced.
Finite element analysis (FEA): Use finite element analysis tools to simulate the stress distribution and vibration characteristics of the frame during the shearing process, identify and optimize high stress areas and vibration hot spots.
2. Introducing vibration-damping materials and damping technology
Vibration-damping pads:
Installing vibration-damping pads (such as rubber pads or composite vibration-damping materials) between the base of the shearing machine and the ground can absorb and disperse vibration energy and reduce the impact of vibration on the equipment and the surrounding environment.
Damping coating:
Coating damping materials (such as viscoelastic coatings or polymer coatings) on the inner surface of the frame can convert vibration energy into heat energy, thereby reducing the vibration amplitude.
Composite materials:
Using composite materials with high damping properties (such as carbon fiber reinforced composite materials) to manufacture some components of the frame can simultaneously improve rigidity and vibration reduction effects.
3. Improve the design of support feet
Adjustable support feet:
Designing adjustable support feet can be adjusted according to the unevenness of the ground to ensure stable installation of the equipment and avoid additional vibration caused by tilting.
Elastic support feet:
Using elastic materials (such as rubber or spring steel) to make support feet can effectively absorb high-frequency vibrations and isolate external vibration sources (such as other equipment or ground vibrations).
Distributed support: Distribute the support feet evenly at the bottom of the equipment and optimize the layout according to the center of gravity of the equipment to balance the load distribution and reduce local vibration.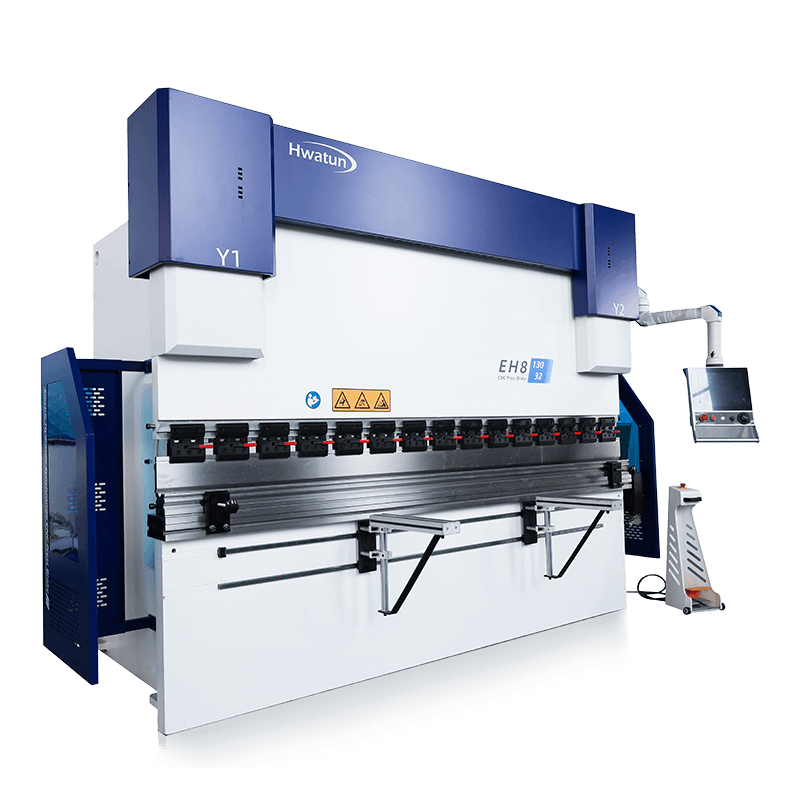
4. Optimize the stability of the hydraulic system
Vibration damping valve: Installing a vibration damping valve or accumulator in the hydraulic system can absorb hydraulic shock and pulsation, thereby reducing vibration caused by hydraulic fluctuations.
Flexible pipeline: Using flexible hydraulic pipelines instead of rigid pipelines can reduce the vibration transmission generated during the flow of hydraulic oil.
Optimize oil circuit design: Reduce fluid turbulence and pressure fluctuations by optimizing the layout of the hydraulic circuit and the selection of pipe diameters, thereby reducing the vibration source.
5. Dynamic balance and inertia compensation
Tool rest balance: Perform a dynamic balance test on the tool rest of the shearing machine, and eliminate the vibration caused by imbalance by adding counterweights or adjusting the mass distribution.
Inertia compensation device: Under high-speed shearing conditions, the vibration during shearing can be offset by adding an inertia compensation device (such as a flywheel or a balance block).
6. Vibration isolation and isolation measures
Vibration isolation platform:
Installing a vibration isolation platform (such as air spring isolator or steel spring isolator) under the shearing machine can effectively isolate external vibration sources (such as ground vibration or vibration of adjacent equipment).
Independent foundation:
Designing an independent foundation structure (such as reinforced concrete base) for the shearing machine and separating it from the surrounding ground can reduce vibration transmission.
7. Improvement of guide rails and sliding components
High-precision guide rails:
Using high-precision linear guide rails or ball guide rails can reduce friction and clearance during tool holder movement, thereby reducing vibration.
Lubrication optimization:
Regularly checking and optimizing the lubrication conditions of guide rails and sliding components can reduce vibration and noise caused by dry friction.
Preload adjustment:
Applying appropriate preload between the guide rail and the slider can reduce looseness and vibration during movement.
Through the comprehensive application of the above methods, the overall vibration resistance of the shearing machine can be significantly improved to meet the processing requirements of high precision and high efficiency.
News categories
Product categories
Related Products
 +86-159 5138 1316
+86-159 5138 1316 +86 180 6819 3096
+86 180 6819 3096 [email protected]
[email protected] Group 4, Xinba Village, Binhai New Area (jiaoxie Town), Laoba Port, Nantong City, Jiangsu, China.
Group 4, Xinba Village, Binhai New Area (jiaoxie Town), Laoba Port, Nantong City, Jiangsu, China.
Copyright © Nantong Hwatun Heavy Machine Tool Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

 Eng
Eng  简体中文
简体中文 Español
Español русский
русский







